Triangulation attack on iPhone using new hardware feature
The Activity Triangulation spyware assaults focusing on iPhone gadgets beginning around 2019 utilized undocumented highlights in Apple chips to sidestep equipment based security assurances.
This finding comes from Kaspersky experts who have been figuring out the perplexing assault chain throughout the last year, attempting to uncover all subtleties that support the mission they initially found in June 2023.
The disclosure and utilization of dark equipment includes likely saved for troubleshooting and processing plant testing to send off spyware assaults against iPhone clients recommend that a modern danger entertainer directed the mission.
Besides, it is a great illustration of why dependence on security through lack of clarity and the mystery of equipment plan or equipment testing execution is a misleading reason.
Activity Triangulation
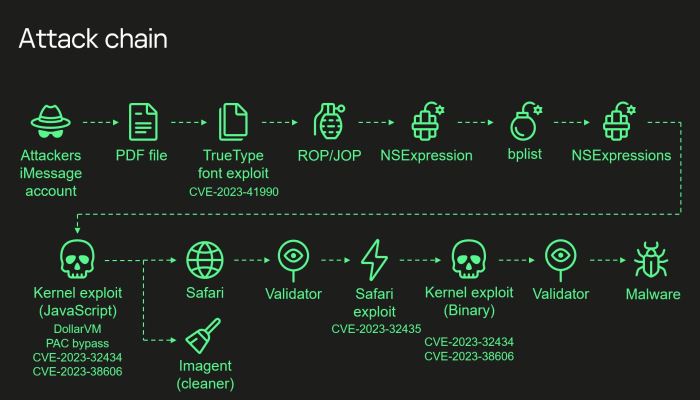
Activity Triangulation is a spyware crusade focusing on Apple iPhone gadgets utilizing a progression of four zero-day weaknesses. These weaknesses are fastened together to make a zero-click exploit that gives aggressors to raise rights and perform remote code execution.
The four blemishes that comprise the exceptionally refined exploit chain and which chipped away at all iOS variants up to iOS 16.2 are:
CVE-2023-41990: A weakness in the Change TrueType textual style guidance permitting remote code execution through a malignant iMessage connection.
CVE-2023-32434: A number flood issue in XNU’s memory planning syscalls, allowing aggressors broad read/compose admittance to the gadget’s actual memory.
CVE-2023-32435: Utilized in the Safari exploit to execute shellcode as a feature of the multi-stage assault.
CVE-2023-38606: A weakness utilizing equipment MMIO registers to sidestep the Page Insurance Layer (PPL), superseding equipment based security assurances.
The assaults start with a noxious iMessage connection shipped off the objective, while the whole chain is zero-clicked, meaning it doesn’t need communication from the client, and produces no recognizable signs or follows.
Kaspersky found the assault inside its own organization, and Russia’s Knowledge Administration (FSB) promptly blamed Apple for furnishing the NSA with a secondary passage against Russian government and consulate faculty.
Up until this point, the beginning of the assaults remained obscure, and there had been no verification of these charges.
Mac fixed the then-perceived two zero-day blemishes (CVE-2023-32434 and CVE-2023-32435) on June 21, 2023, with the arrival of iOS/iPadOS 16.5.1 and iOS/iPadOS 15.7.7.
Profoundly complex assaults
Of the above blemishes, CVE-2023-38606, which was tended to on July 24, 2023, with the arrival of iOS/iPadOS 16.6, is the most charming for Kaspersky’s investigators.
Taking advantage of the imperfection permits an assailant to sidestep equipment insurance on Apple chips that keep aggressors from acquiring unlimited authority over the gadget when they gain read and compose admittance to the bit memory, which was accomplished utilizing the different CVE-2023-32434 blemish.
In the profound jump specialized writeup, Kaspersky makes sense of that CVE-2023-38606 targets obscure MMIO (memory-planned I/O) registers in Apple A12-A16 Bionic processors, reasonable connected to the chip’s GPU co-processor, which are not recorded in the Device Tree.
Activity Triangulation utilizes these registers to control equipment elements and control direct memory access during the assault.
“In the event that we attempt to depict this element and how the assailants exploited it, all that matters is this: they can compose information to a specific actual location while bypassing the equipment based memory security by composing the information, objective location, and information hash to obscure equipment registers of the chip unused by the firmware,” makes sense of Kaspersky’s report.
Kaspersky guesses that including this undocumented equipment highlighted on the completed purchaser’s rendition of the iPhone is either an error or was left in to help Apple engineers with troubleshooting and testing.
Apple fixed the imperfection by refreshing the gadget tree to confine actual location planning.
In any case, how the aggressors acquired information on such a dark exploitable system in any case stays obscure.

